Unlocking the Language of Dogs
Understanding a dog's behaviour and communication is essential for pet owners and caretakers alike. Dogs use a variety of signals, both vocal and physical, to express their feelings and needs. While some of these behaviours can be shaped through training, they may also be influenced by breed characteristics. By recognising and interpreting these signals, owners can strengthen their bond with their dogs and promote their overall wellbeing.
The Power of Body Language
Canine body language is a complex yet fascinating aspect of canine communication. From the positioning of their ears and tails to their facial expressions, dogs convey a wealth of information through their posture. Recognising signs of relaxation, stress, or aggression can help us to respond appropriately and nurture a safe environment.

Social Signals Among Dogs
Interactions between dogs can be equally as telling. Dogs utilise a rich set of social signals to communicate with one another, including play bows, sniffing, and even facing away as a sign of submission. Being aware of these cues can significantly improve our understanding of how dogs socialise, and how they relate to their human counterparts.
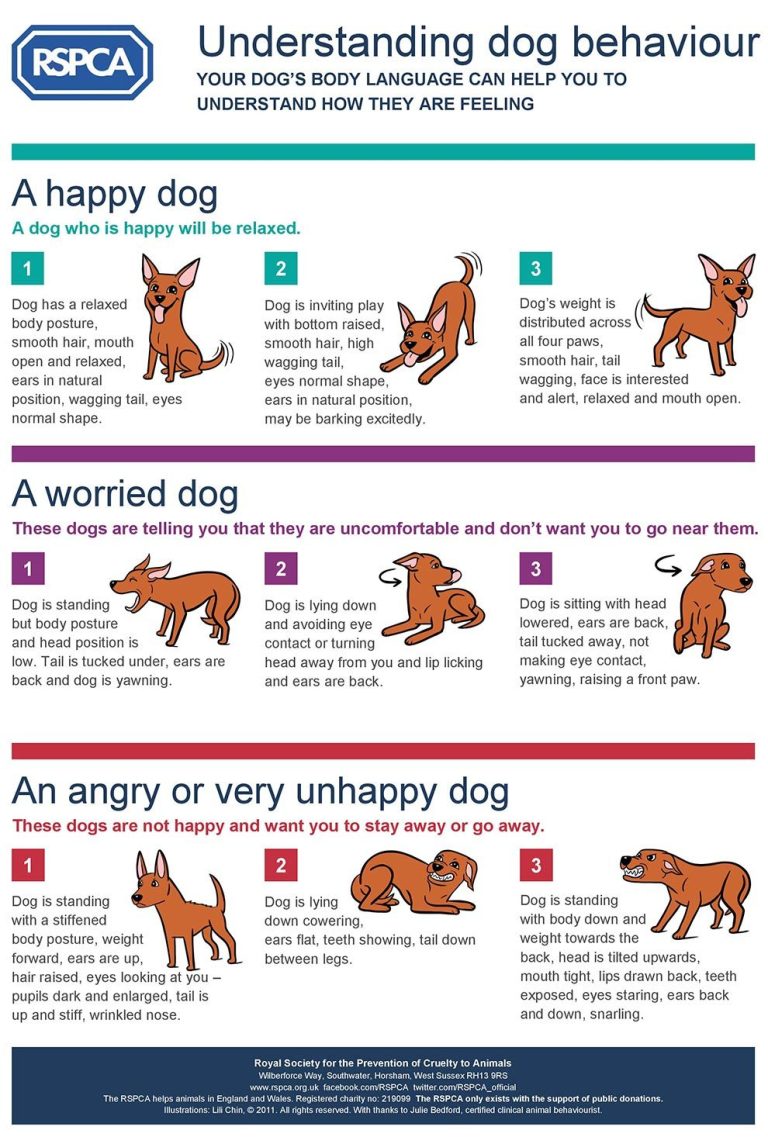
Common Signals and Their Meanings
This article provides an overview of canine behaviour and emotions, as outlined by the RSPCA. Understanding these aspects is essential for pet owners and those working with dogs. Canines communicate their feelings through body language, vocalisations, and actions. Key indicators of a dog’s emotional state include tail position, ear orientation, and facial expressions. Aggression, fear, and anxiety can arise from various factors, such as lack of socialisation, a traumatic experience, or environmental changes. Recognising these signs allows for better management of a dog’s well-being. By fostering a safe and supportive environment, owners can enhance their dogs’ quality of life and strengthen their bond. The RSPCA emphasises the importance of positive reinforcement training to promote desirable behaviour and emotional stability in dogs.
How Do Dogs Learn?
Dogs can learn by associating their actions with specific outcomes. One key aspect of this learning process is positive reinforcement, where rewarding desired behaviours encourages dogs to repeat those behaviours. Additionally, effective training relies on consistency in commands and expectations, precise timing of rewards or corrections, and maintaining the dog's motivation to learn. Understanding these elements is essential for successful dog training.
*Always consult a veterinary professional if you are concerned about your dogs behaviour. Vets are well placed to refer you to a certified dog trainer or behaviourist.
1.
Learning Through Reinforcement
Positive reinforcement is a training method that encourages desired behaviours by providing rewards, thus increasing the likelihood of those behaviours being repeated. Rewards can take various forms, including food, verbal praise, toys, or engaging in play activities. For instance, offering a small food treat when a dog sits on command effectively reinforces the behaviour and makes it more likely to occur again in the future.
3.
Understanding the Dog's Perspective
Motivation is essential in dog training, as dogs respond to various incentives. Identifying what specifically motivates your dog can enhance the effectiveness of behaviour improvement efforts. Additionally, dogs require clear and consistent cues and signals to understand what is expected of them. Training necessitates time and patience; it is important to remain persistent and not to feel disheartened if your dog does not master a new behaviour right away.
2.
Consistency & Timing
Dogs benefit significantly from a structured and predictable environment. It is essential to use the same commands, cues, and consequences consistently to help prevent confusion in your dog. Additionally, timing plays a vital role in training; rewarding desired behaviours promptly allows the dog to effectively associate the behaviour with the reward.
4.
Socialisation & Habituation
Introducing your dog to a diverse array of individuals, animals, and environments during their formative puppy stage is essential for their development into well-adjusted adult dogs. Habituation plays a critical role in fostering healthy behavioural patterns. This process involves acclimatising a dog to new situations or objects through gradual exposure. For example, allowing a pet carrier to remain visible within the living space or keeping the door ajar enables the animal to become familiar with its presence.
